One of the principles of the 3 2 1 rule of backup storage is that you should have one backup copy off site. Great but for code this can be tricky as you constantly need to be changing so how do you set up a continuous pipeline to allow for changes in code. Now you could use something like Google Cloud which is excellent and is completely acceptable however I wanted to use GIT mainly because it is better adapted to actually editing code if needed be (important for removing security parameters in things like webconfig files) , has finer grained level of detail in terms of control and is considered a professional format for storing code and version code. Of course with greater flexibility comes great complexity. So here are my beginnings on using GITHub.
First things first register with GITHub
I would then recommend that you download Git Bash – this is a local program that will allow you to better synch your files between your development machine and your online github repository. I found the following Video Tutorial excellent in getting up and running in particular in downloading and installing GITHub Bash and linking it to your GITHUB repository.
GIT Hub (Good Tutorial on starting out)
Now here I am going to setup my local repository’s in the root directory and simply call the directory git
c:/git
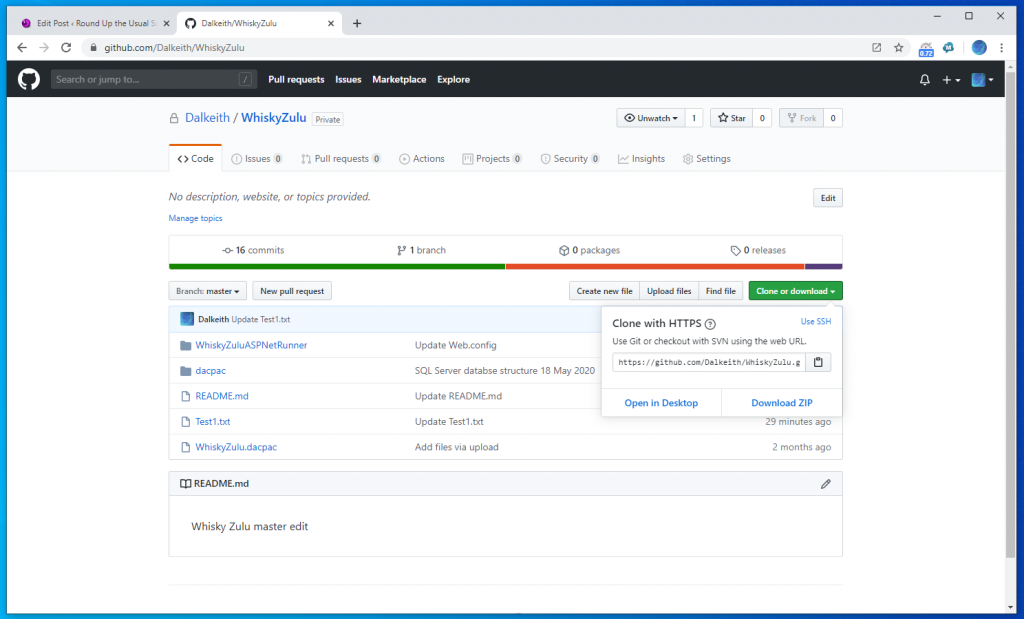
For my purposes I have started by create a repository in online GITHUB
The open GITBASH
You will be presented with the following window
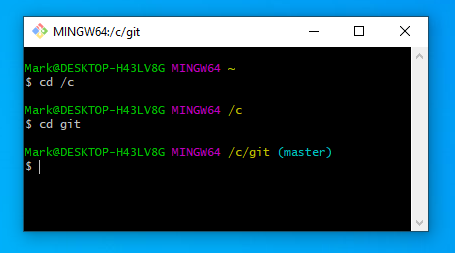
The first tricky thing is to navigate the bash prompt
execute the following commands
cd /c
cd git
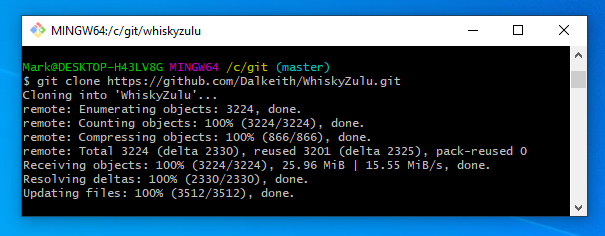
Next we are going to Clone a repository from out GITHUB web account to our local machine.
Cloning does two main things it creates a sub-directory in this case within the c:\git directory and then copies all the files down from the web repository.
The command to do this is
git clone (followed by the url of your repository obtained here)
and execute it something similar to the below should now appear – a new sub directory should appear on your local machine with all files within it. Congratulations you have just downloaded all these files you could do this with any open source project on GITHub
Next lets see how we can download from the website masters or alternatively upload from local.
You might be thinking well why do I want to upload from local when I see that you can cut and paste directly into the web browser and commit from there. Yes good but the browser user interface won’t allow you to transfer more than 100 files which for web applications is a killer.
Now the same thing can be done with whole directories so simply use explorer to upload the item into the local directory and then push from there.
OK uploading from LOCAL
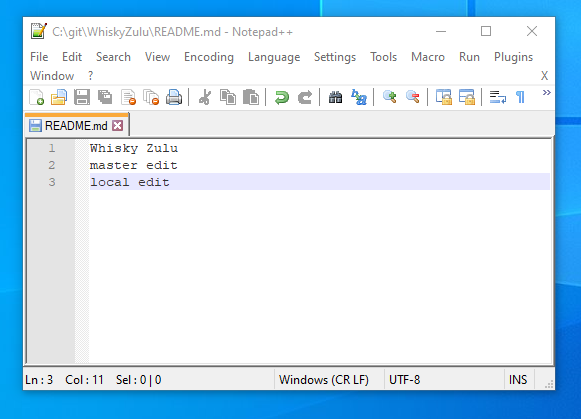
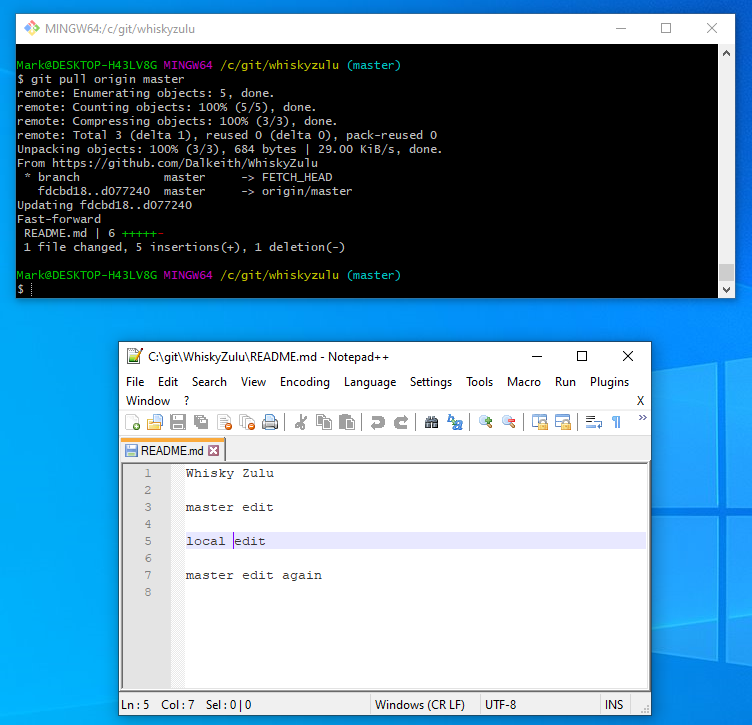
As an example lets make a change to the readme file and try and get it to be accepted onto our online account.
Got to your new directory and edit the README.md file in your editor of choice with some kind of change.
eg
Now back in bash perform the following;
Navigate to the directory and if the file was already
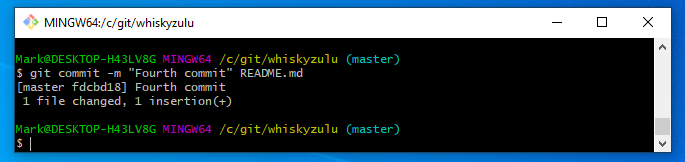
git commit -m “Fourth commit” README.md
This has committed the change in that particular file to the local git repository – this is important without a commit git doesn’t know anything has changed. Next you want to commit the local to the master web version
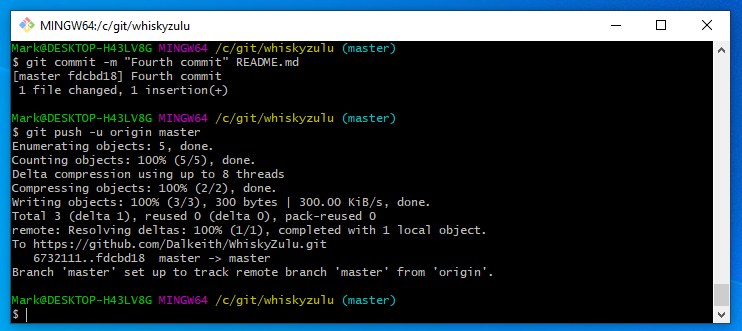
Execute the following command
git push -u origin master
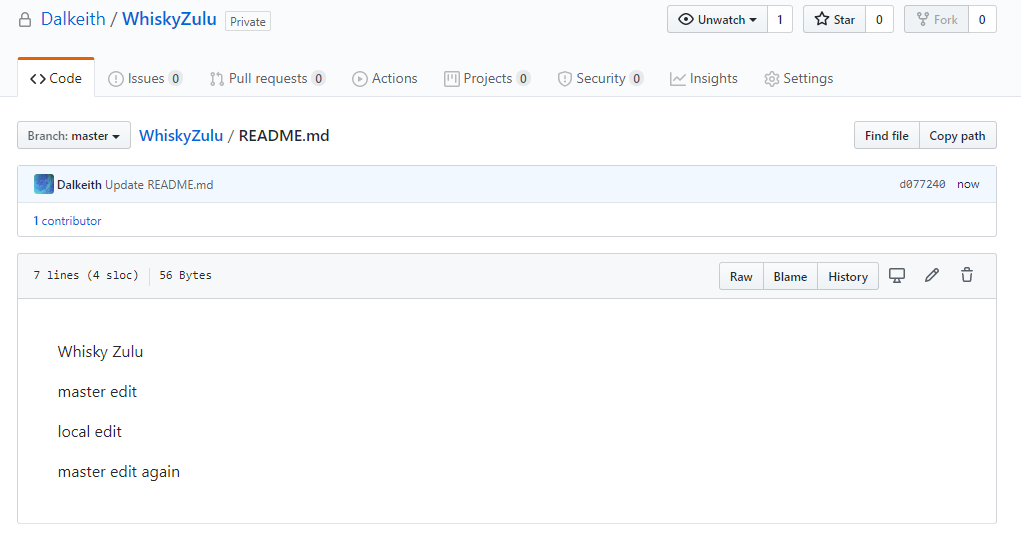
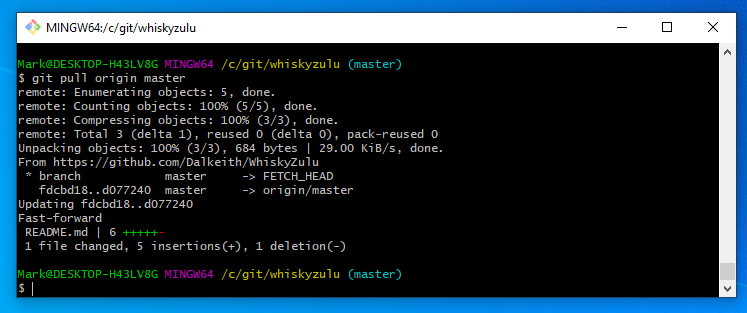
Now you can go to your web repository and you should see that README.md has changed
Now the same thing can be done with whole directories so simply use explorer to upload the item into the local directory and then push from there.
DOWNLOADING changes from GITHub Repository to local.
This time lets make an edit to GITHUB README.md through the web repository commit it
And we see that local has now been updated with the web repository
But what if we need to add a complete directory or a file to local and then upload it.
Here we first need to add the directory or file to local
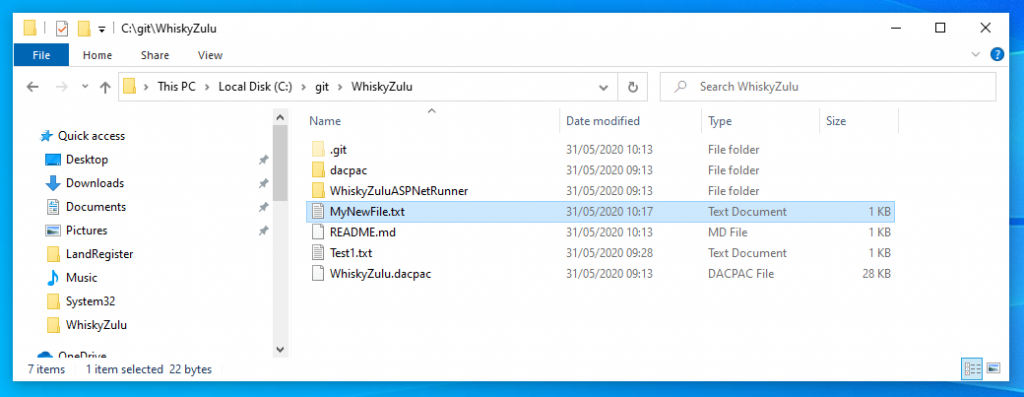
For example create a new file in the local directory called MyNewFile.txt
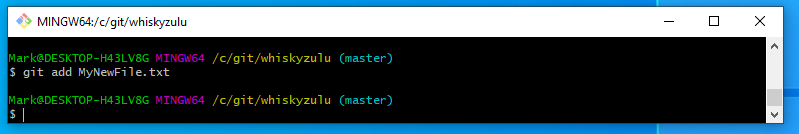
git add MyNewFile.txt
Before transfering this file to your github account you need to commit it first.
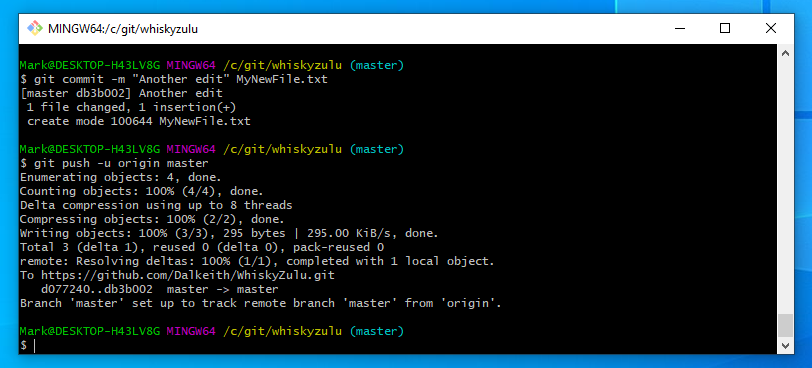
git commit -m “comment message” MyNewFile.txt
you then need to push this to your Git hub account
git push -u origin master
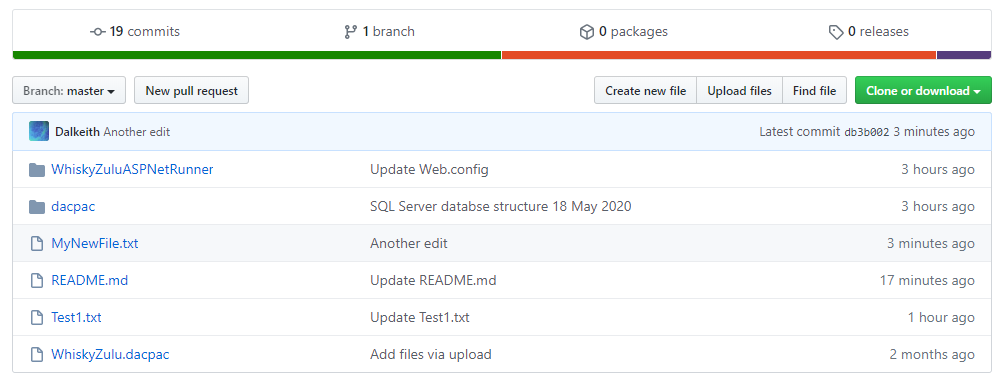
Going back to your GIT Hub repository on your account and refreshing the screen you should see the item.
The above processes should get you started with GITHUB if things start to go wrong with errors try the below.
Note it would appear that if you wish to overwrite a local file or directory and then add it to your remote repository you still have to go through the ADD procedure. (Initially I had assumed that because a directory might already be there you might not need to add it)
So if you were going to overwrite the output folder it would be a case of
git add -A
git commit -m "Output file overwritten"
git push origin master
REMOVING a repository and starting again..
Removing a repository from local which can be useful if like me you make changes to local and web version independently and it has issues merging the two and prevents the merge and starting out wasn’t sure how to fix everything maunally. I found the easiest way was to make sure you were happy with the online version. Delete the local copy and then clone to local again.
Firstly navigate to the repository directory you wish to delete and then
$ rm -rf .git
Now you can delete the directory and go forward but remember you will need to Clone the repository and start from there.