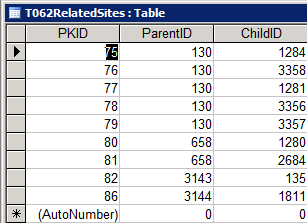
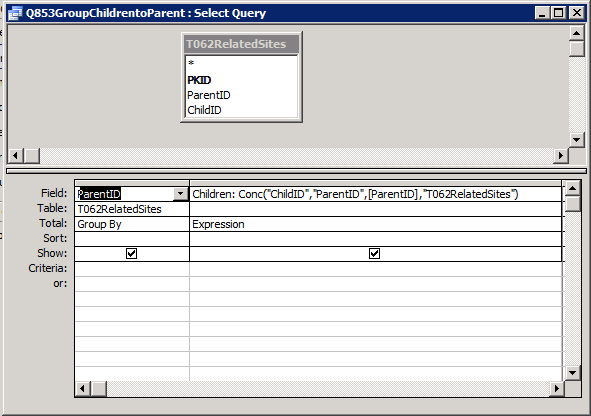
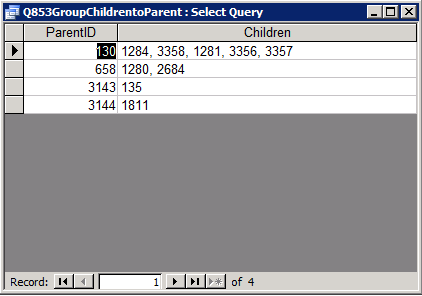
A while back I wrote a post about how allowing parameters to be passed to URLs is a big benefit in increasing the speed with which you can navigate to individual records in apparently non-connected web applications.
But what do you do if you are faced with a satellite application whose vendor has not implemented this URL friendly facility. Users are left with the very jarring break to the flow of their work when they have to leave the application they are in and navigate to another application sometimes manually having to link to the other application records form via a search field. This searching task when multiplied many times can be really tedious, repetitive, demotivating and time consuming not to mention pointless.
How can we better serve our users?
The other day I came across an open source program called AutoHotKey that allows me to improve this task.
AutoHotKey
Autohotkey is an open source project that allows the creation and compilation of simple or complicated scripts that can be used to navigate anything on a computer. That means desktop OR web applications. The following is something that I worked out last week to be able to navigate a web application by triggering a script from MS Access vba. The great thing is that you can pass parameters from a database application to a middle layer and trigger a set of commands to be run.
Let us take the example of a recent problem I faced. Many councils throughout the United Kingdom have bought an application from a company that manages the information associated with making planning applications, it consists of both desktop and web applications that help manage the submission and decision making associated with development. The vendor recently “upgraded” the application resulting in it no longer accepting planning application numbers to its URL as a method of going straight to the record. This was meaning that users of one of my satellite applications were faced with being dropped into a search screen and then needing to manually type a field from one application into the field of another application. QED dull and repetitive task.
There follows and overview of my solution. Firstly download the following programs
1)AutoHotKey
AutoHotKey
2)iWB2 Learner – which is a small program for identifying element names and id in INTERNET explorer.
iWB2 Learner
iwebbrowser2 Download
My script for Autohotkey was as follows.
FindRecordReference.ahk (written in plain old notepad and saved to a known location with the suffix changed to ahk)
=====================
APPLICATION = %1%
URL := "https://onlinerecordset/"
WB := ComObjCreate("InternetExplorer.Application")
WB.Visible := True
WB.Navigate(URL)
While wb.readyState != 4 || wb.document.readyState != "complete" || wb.busy ; wait for page to open
Sleep, 10
wb.document.getElementById("simpleSearchString").value := Application
wb.document.getElementsByTagName("INPUT")[4].Click()
While wb.readyState != 4 || wb.document.readyState != "complete" || wb.busy
Sleep, 10
return
===================
Using iWB2 Learner to identify the element names on the web page
This video shows iWB2 Learner being used it unfortunately does not have any sound.
VIDEO Using iWB Learner with AutoHotKey
—-
Next you will need to trigger the AHK – You will need design access to the program that is sending the instruction to do this. In my MS Access application I have the following code that triggers the script in the above.
Private Sub Command43GoToOnlineRecord_Click()
Dim strRecordNo As String
Dim strAHKname As String
strPlanApp = "LIVE/" & Me.RecordNo
strAHKname = "\\[YourServerName]\FindRecordReference.exe"
Call Shell(strAHKname & " " & strRecordNo, vbMaximizedFocus)
End Sub
Notes:
The computer that holds the AHK script need not have AutoHotKey installed if it doesn’t you can compile your script into an executable that will not require installation. Here I created the executable on another computer and transferred it to the \\server1-cluster\ahk location ready to be called by the VBA
Consecutive parameters passed to Autohokey are consecutively named %1% %2% etc.. In my script I pass the planning application as %1% and rename it APPLICATION immediately.
Compiling the AHK is done by moving to a computer with AHK installed and navigating in Explorer to the file and then right click and Compile will be an option. Note the processor architecture is important when compiling. If your target machine is 32bit then you need to compile on a 32bit machine – same with 64.